Hydrograph flood
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
Have you ever wondered how to draw a flood hydrograph? A flood hydrograph is a graph that shows the rate of flow versus time of a river in response to a storm event. Understanding how to draw a flood hydrograph is crucial for anyone studying or working in fields related to water management, environmental science, or civil engineering. In this blog post, we will go over the steps needed to draw a flood hydrograph, as well as provide some personal experiences we have had with creating these graphs.
When it comes to drawing a flood hydrograph, there are a few pain points that may arise. These can include not being familiar with the necessary data and not understanding the hydrograph’s purpose or components. It can also be challenging to choose the appropriate scale or decipher and analyze the graph’s resulting data points.
To draw a flood hydrograph, you will first need streamflow data, typically measured from a streamflow gauge station. Once you have the dataset, you can begin plotting the hydrograph. In general, flood hydrographs typically show two curves: one representing the water level’s rise, and the second curve showing the water level drop. The key components of a flood hydrograph include the flood peak discharge, lag time, and rising limb and falling limb.
In summary, to draw a flood hydrograph, you will need a dataset, understanding of the hydrograph’s components, and knowledge of the necessary graphing tools.
How to Draw a Flood Hydrograph: Personal Experiences
As someone who has studied water management, I have had some experience creating flood hydrographs. I recall a time where we were tasked to analyze the effects of an urbanization event on a local waterway. The goal was to see how land-use changes would impact the downstream hydrograph. I gathered data from the streamflow gauge station above the development area and below the area. I then plotted the data points on graph paper and drew the hydrograph. It was challenging to choose an appropriate scale and decipher the hydrograph’s components, but once I had a grasp of these, I was able to create an effective hydrograph to present my findings.
Tools Used to Draw a Flood Hydrograph
The necessary tools to draw a flood hydrograph are available both online and offline. Graph paper, a ruler, and a pen can be used for any manual drawing. Some online tools that can be used include Hydrographer, HydrographJS, and USGS Water data for the nation. For graphing software, you can use Excel or specialized hydrographing software such as Hydrograph or HEC-RAS.
Understanding the Components of a Flood Hydrograph
A flood hydrograph is made up of several components that are important to know for accurate graphing. The rising limb illustrates how the water level in a river increases to reach its peak flow during a flood event. The flood peak discharge shows the maximum rate that the water level was rising during the flood event. The lag time depicts the time between the storm event’s peak and the peak of the flood wave. Lastly, the falling limb represents the water level receding after the peak flow.
Tips and Tricks for Drawing a Flood Hydrograph
When drawing a flood hydrograph, it’s important to choose an appropriate scale that fits the dataset. Additionally, labels, units, and a legend must be included to help visualize the data. Interpretation of the resulting data points is also critical; interpret the data points based on the hydrological information known to make practical recommendations.
Question and Answer
Q: What is a flood hydrograph?
A: A flood hydrograph is a graph that shows the rate of flow versus time of a river in response to a storm event.
Q: What are the key components of a flood hydrograph?
A: The key components of a flood hydrograph include the flood peak discharge, lag time, and rising limb and falling limb.
Q: What is the purpose of creating a flood hydrograph?
A: The purpose of creating a flood hydrograph is to analyze a river’s response to a storm event and to identify the peak flow and lag time.
Q: What tools can be used to draw a flood hydrograph?
A: Some tools that can be used to draw a flood hydrograph include graph paper, a ruler, and pen, and specialized software like Hydrograph, HEC-RAS or Hydrographer.
Conclusion of how to draw a flood hydrograph
Drawing a flood hydrograph can be overwhelming, but having the right tools, such as graph paper or specialized software, and understanding the hydrograph’s components can make it more manageable. With practice, drawing flood hydrographs can become a more straightforward process, which can lead to better water management decisions and insights into river ecosystems.
Gallery
2. The Drainage Basin – MrB Geography IB

Photo Credit by: bing.com / hydrographs river hydrograph geography level gcse storm discharge factors affecting draw processes pressures floods aqa
Simple Flood Hydrograph | Download Scientific Diagram

Photo Credit by: bing.com / hydrograph flood
Hydrographs
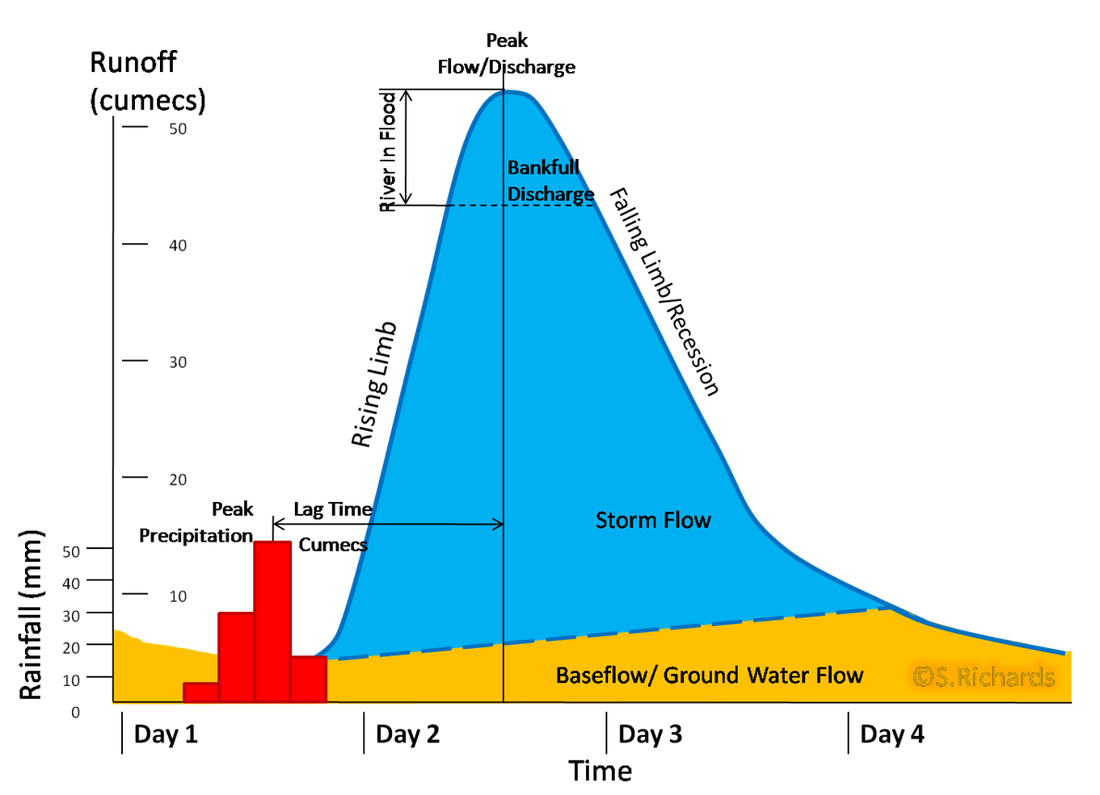
Photo Credit by: bing.com / hydrograph storm river discharge hydrographs regime geography peak graph flood annotated flow limb definition gcse lag weebly rainfall environment water
Typical Hydrograph For Urban And Rural Runoff This Hydrograph Shows The

Photo Credit by: bing.com / hydrograph runoff volume peak discharge streamflow lag
Typical Flood Hydrograph. | Download Scientific Diagram

Photo Credit by: bing.com / hydrograph flood