10 strike network diagram
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
Are you struggling with mapping out your network infrastructure? Do you want to create a clear and organized diagram of your devices, connections, and protocols? Drawing a network map might seem daunting, but it doesn’t have to be. In this article, we’ll guide you through the process of creating a network map, so you can improve your network management, troubleshooting, and security.
The Pain of Network Map Drawing
Keeping track of your network components and their interactions can be a real headache, especially if you have a large, complex network. Without a visual representation of your topology, you might miss out on vital information, such as outdated hardware, bottlenecks, or vulnerabilities. You could also waste time and effort trying to manually trace cables or identify devices. Moreover, if you don’t have a standardized and updated network map, you might face difficulties in communicating with your team, stakeholders, or vendors, leading to mistakes, misconfigurations, and ultimately, downtime or breaches.
How to Draw a Network Map
The good news is that drawing a network map is not rocket science. There are several methods and tools you can use, depending on your network type, size, and goals. Here are the general steps that you can follow:
- Identify the scope and purpose of your network map. Do you want to show the physical topology, logical topology, or both? Do you want to focus on a part of the network, such as a subnet, a floor, or a department? Do you want to use the map for monitoring, provisioning, documentation, or planning?
- Scan your network to gather information about your devices, IP addresses, MAC addresses, and interfaces. You can use a network scanner, such as Nmap, SolarWinds, or Lansweeper, to automate this process or do it manually.
- Create a rough sketch of your network map, using a pencil and paper or a digital whiteboard. You don’t have to be precise at this stage, as you’ll refine your map later, but you should include the main elements, such as routers, switches, firewalls, servers, workstations, printers, and wireless access points.
- Choose a network mapping tool that suits your needs and budget. There are many paid and free options, such as Lucidchart, draw.io, PingPlotter, or Microsoft Visio. Look for a tool that supports your network protocols, has a user-friendly interface, allows collaboration and sharing, and integrates with your other tools.
- Import your network data into your mapping tool, or enter it manually. This step might take some time, depending on the accuracy and completeness of your data, and the complexity of your network. Make sure to label your devices and connections clearly, using logical naming and color codes.
- Refine your network map, by adjusting the layout, highlighting the critical paths, adding annotations and legends, and customizing the design. You can also use some advanced features, such as auto-discovery, alerts, reports, or simulations, to improve your network analysis and management.
- Share your network map with your team, stakeholders, or vendors, by exporting it to various formats, such as PDF, SVG, PNG, or HTML. Get feedback and make changes if necessary, before you finalize your map and archive it.
Summary of Network Map Drawing
In summary, drawing a network map can help you visualize your network, diagnose problems, plan upgrades, and communicate effectively. To draw a network map, you need to define your goals, scan your network, sketch your map, choose the right tool, import your data, refine your map, and share it with others. By following these steps, you can create a reliable and up-to-date network map, that saves you time, money, and headaches.
Best Practices for Network Map Drawing
While the steps above can guide you in creating a network map, there are certain best practices that you should follow to ensure its effectiveness and efficiency:
- Be consistent and standardize your naming conventions, IP addressing, and protocols. This will make it easier for you and others to understand and manage your network.
- Update your network data regularly, by using automated tools, manual checks, or a combination of both. Don’t rely on outdated information, as it might cause errors and security risks.
- Use color codes and symbols wisely, to convey meaning and avoid confusion. For example, you can use green for healthy devices, red for alarms, blue for VLANs, or arrows for traffic flows.
- Document your network map, by adding descriptions, legends, or notes. This will help you and others to interpret your map’s context, purpose, and limitations.
- Integrate your network map with your other tools, such as monitoring, ticketing, or CMDB. This will enable you to correlate your network events and actions, and streamline your workflows.
The Benefits of Network Map Drawing
By following these best practices, you can reap the benefits of network map drawing, such as:
- Improved network visibility, performance, and security
- Reduced downtime, troubleshooting, and risk of data loss or theft
- Streamlined communication, collaboration, and compliance
- Enhanced planning, forecasting, and optimization
- Better alignment with your business goals and needs
My Experience with Network Map Drawing
As a network engineer, I’ve had my fair share of challenges when it comes to network map drawing. I remember one instance, where I had to troubleshoot a server that was intermittently losing connectivity. It took me hours to figure out that the issue was caused by a misconfigured switch port, which was blocking the server’s VLAN. If I had a network map at the time, I could have spotted the problem much faster and avoided the downtime.
Another example was when I had to redesign a client’s network, after they had suffered a ransomware attack. They had no network map, and their IT staff had to rely on memory and scraps of paper to identify the infected machines and segregate them. It was a chaotic and stressful situation, that could have been prevented if they had a network map in the first place.
Nowadays, I use a combination of manual and automated approaches to drawing a network map, depending on my clients’ preferences and requirements. I find that using a digital tool, such as Lucidchart or draw.io, saves me a lot of time and effort, and allows me to collaborate with others seamlessly. I also make sure to keep my network data up-to-date, by using a network scanner, such as Nmap, and integrating my map with my monitoring system, such as PRTG.
Questions and Answers
Here are some common questions and answers related to how to draw a network map:
Q: What should I include in my network map?
A: You should include at least the following elements in your network map: routers, switches, firewalls, servers, workstations, printers, and wireless access points. You should also label your devices and connections clearly, and indicate their status, such as active, inactive, or faulty.
Q: How often should I update my network map?
A: You should update your network map regularly, depending on the changes in your network. It’s recommended to update it at least once a month, or whenever you add or remove devices, make configuration changes, or face network issues.
Q: Can I draw a network map manually?
A: Yes, you can draw a network map manually, using a pencil and paper or a digital whiteboard. However, this method is less efficient and less accurate than using a dedicated network mapping tool, as it requires more time and can lead to errors and omissions.
Q: How can a network map help me with security?
A: A network map can help you with security in several ways, such as:
- Identifying potential attack vectors, such as open ports, outdated software, or weak passwords
- Monitoring suspicious traffic patterns, such as abnormal flows, spikes, or drops
- Visualizing your security posture, such as your firewalls, antivirus, or encryption
- Planning and testing your security measures, such as incident response, disaster recovery, or penetration testing
Conclusion of How to Draw a Network Map
Drawing a network map might seem overwhelming at first, but with the right guidance and tools, it can be a simple and rewarding task. By following the steps we outlined in this article, you can create a network map that meets your goals and standards, and helps you manage your network more efficiently and effectively. Remember to follow the best practices we shared, and to keep your network data up-to-date and accurate. Happy mapping!
Gallery
Custom Network Maps & Business Views | ManageEngine OpManager
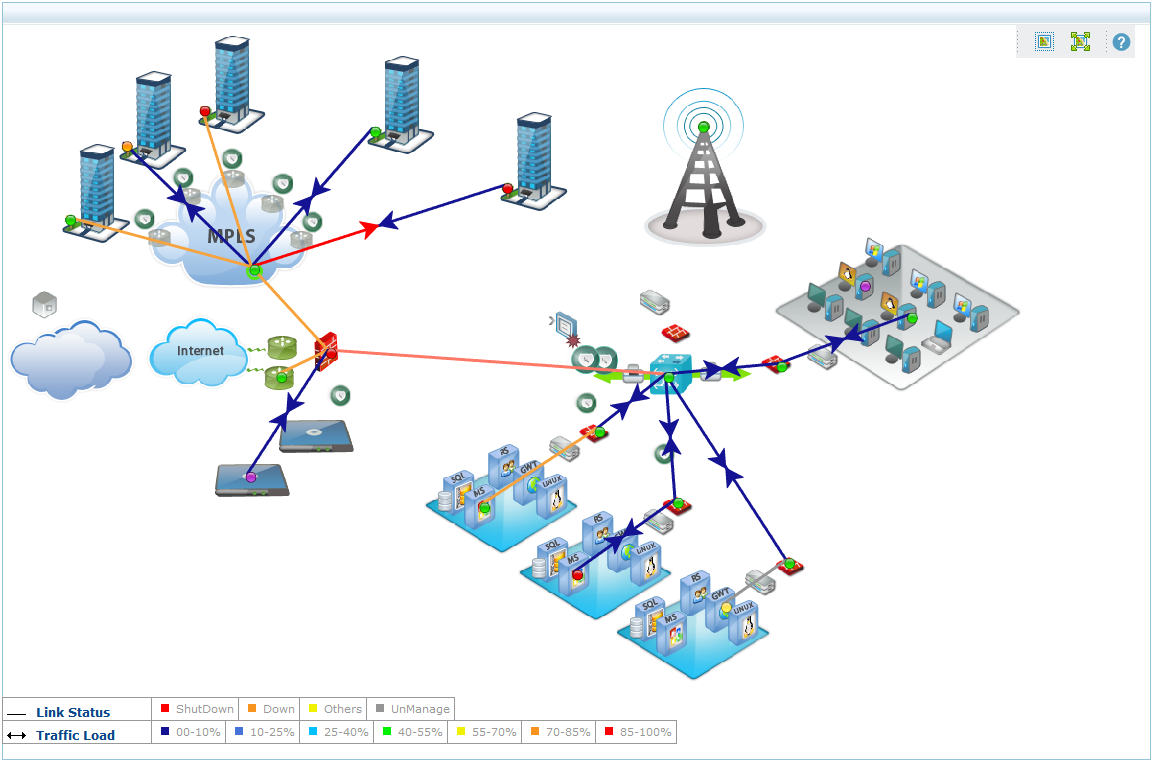
Photo Credit by: bing.com / network opmanager map mapping manageengine private enterprise software monitoring maps monitor infrastructure tool performance services business computer company locations maker
Hotel Network Topology Diagram
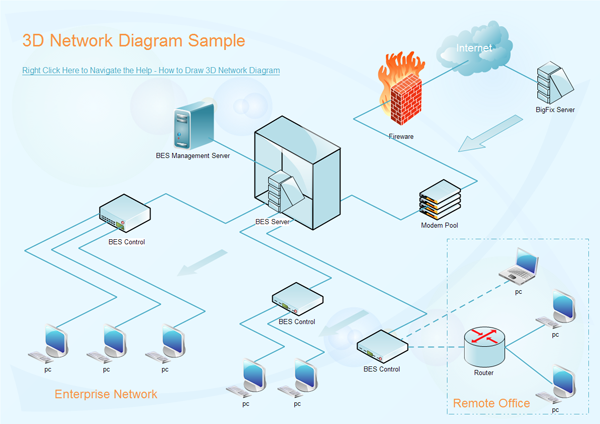
Photo Credit by: bing.com / network 3d software diagram topology examples edraw example template templates create complete sample draw simple mapper hotel solarwinds systems links
Network Topology Mapper Free - Mixbrown

Photo Credit by: bing.com / network topology maps mapper dynamic mapping networking map tool software netbrain change update solarwinds automatically re auto answer ask question
10-Strike Network Diagram:
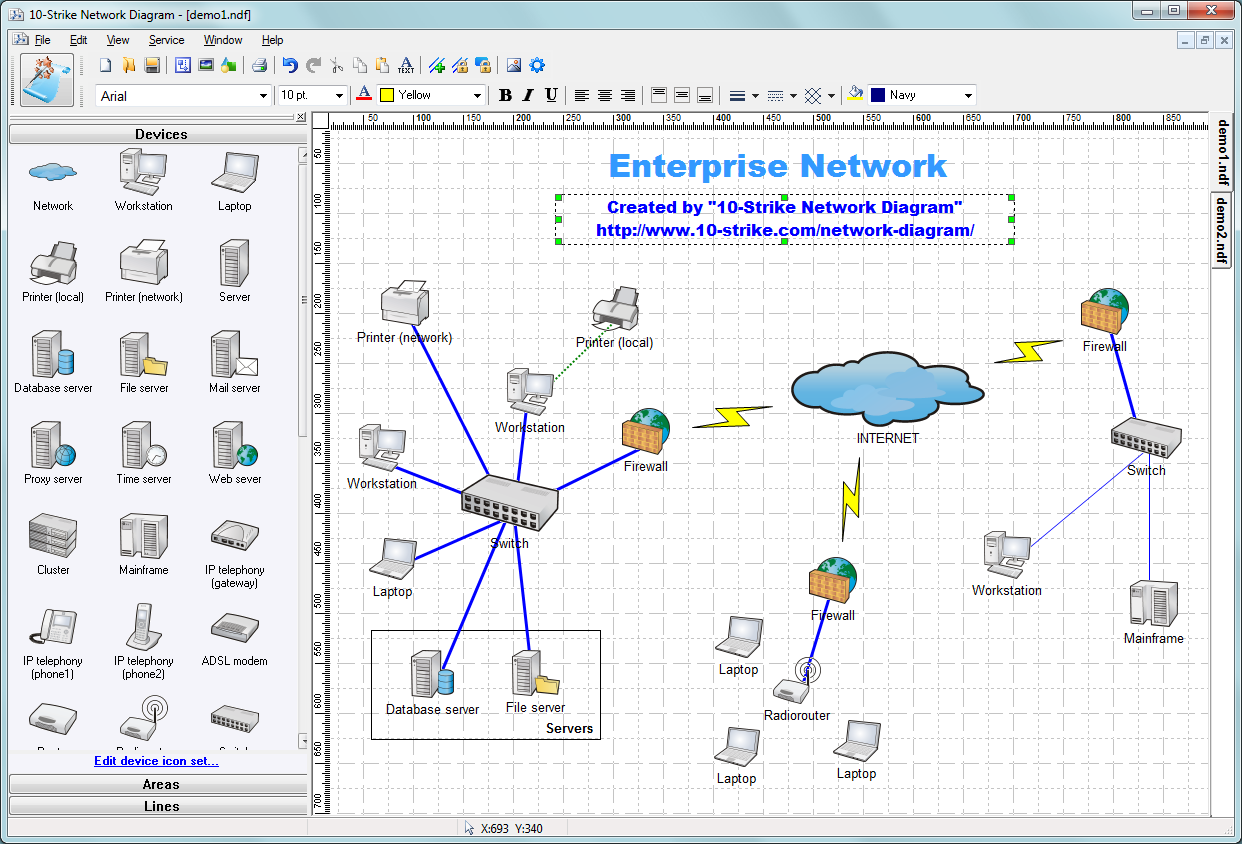
Photo Credit by: bing.com / visio topology strike tool diagrammer schematic template erstellen automatically crack rete schema instalki voip redes mappatura mapper sieci dnsstuff downloaden
Network Diagram Drawing At GetDrawings | Free Download
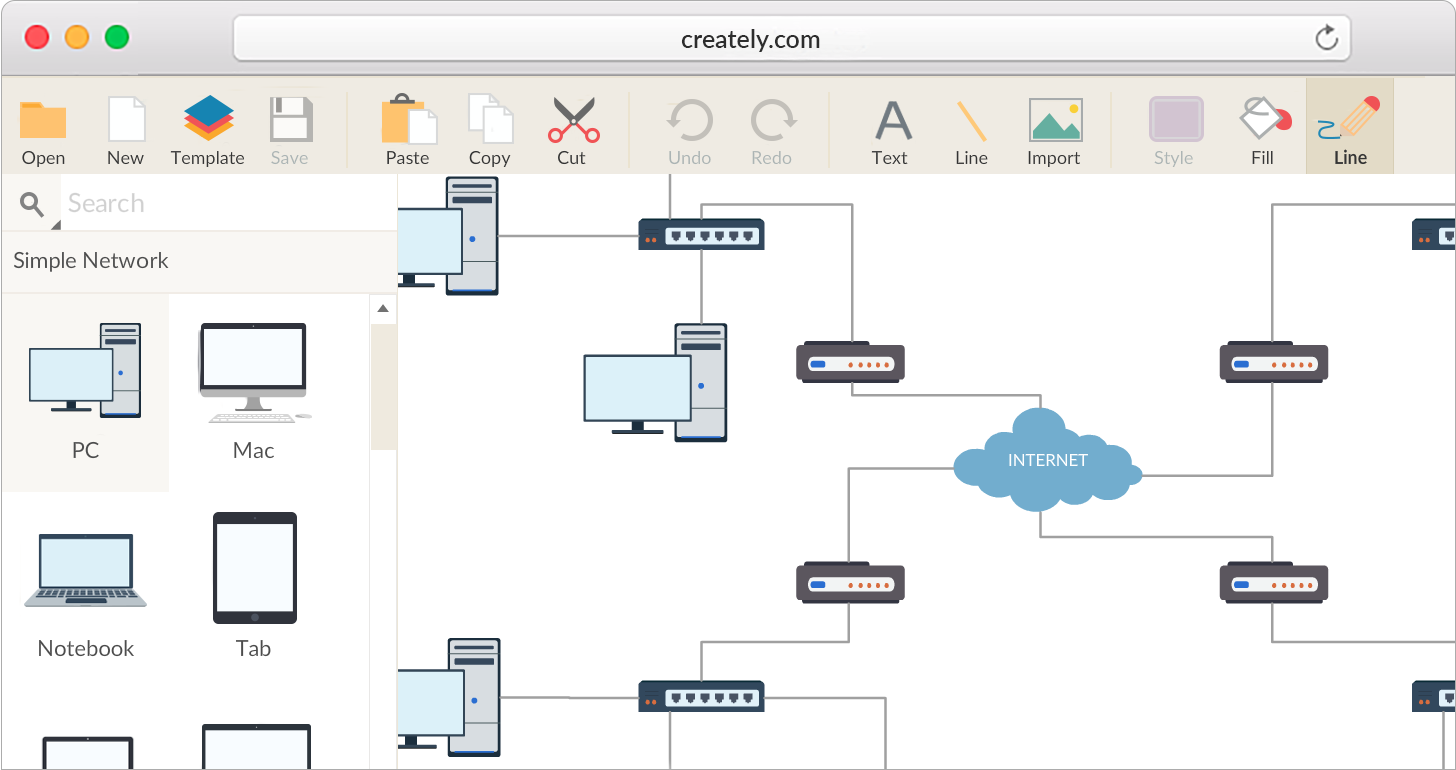
Photo Credit by: bing.com / network diagram software drawing source diagrams plan open diagramming draw project create tool building using line house make detailed